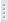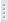Butane - Heat and Dispatch
Jiří Patočka
Butane
(C4H10)
is a colorless, flammable hydrocarbon that is present
in natural gas and can be obtained when petroleum is refined. Butane is a gaseous
alkane. It is extremely stable, has no corrosive action to metal,
slightly soluble in water and readily soluble in alcohol, ether and chloroform.
Butane is widely used in the manufacture such as aviation fuels and organic
chemicals, a raw material for synthetic rubber and high octane liquid
fluids, etc. Butane exists as two isomers: n-butane
is a fully hydrogenated linear chain of four carbon atoms: CH3CH2CH2CH3
and isobutane, has the formula CH3CH(CH3)2,
and the systematic name 2-methylpropane. Recent concerns about the destruction of
the ozone layer by freon gases has led to an increase use of isobutane gas in
refrigerating systems.
Butane is a
simple asphyxiant with explosive and
flammable potential but all the time was rate as non-toxic compound. In recent
years butane is also widely used substance of abuse. The main target organs are
in the central nervous and cardiovascular system. Abuse of butane is extended
between young people. Its innitial effects are euphoria, excitation, blurred
vision, slurred speech, nausea, vomiting, coughing, sneezing, and increased
salivation. As its dose increases, disinhibition, confusion, perceptual distortion,
hallucinations (ecstatic or terrifying), delusions (which may lead to
aggressive or risk taking behaviour), tinnitus, and ataxia come out. Large
doses induced nystagmus, dysarthria, tachycardia, central nervous system (CNS)
depression, drowsiness, coma and sudden death which may result from anoxia,
vagal inhibition of the heart, respiratory depression, cardiac arrhythmias or
trauma. Butane inhalation can cause serious medical complications and is
particularly toxic to the nervous system. Namely children are very sensitive.
Many children died
from self-induced butane inhalation. Recently was investigated and reported
case of the deaths of six young New Zealanders due to butane inhalation
(Decisions 86-91/05, 26 September 2005). These deaths occurred between January
2003 and April 2004 in
people aged 15–27 years. The reports are compelling reading and strong
recommendations are made about the management of drug abuse in New Zealand.
These reports had widespread attention in the national media. The following is
a brief overview of the clinical pharmacology of abused inhalants, in
particular the properties and actions of butane. Relatively frequent are these
intoxications in Japan. Similar cases are known but not so widespread discussed
in Czech Republic.
References
Kile SJ, Camilleri CC, Latchaw RE, Tharp BR. Bithalamic lesions of butane encephalopathy. Pediatr. Neurol. 2006 35, 439-441.
Nishi K, Ito N, Mizumoto J, Wada K, Yamada T, Mitsukuni Y, Kamimura S. Death associated with butane inhalation: report of a case. Nihon Hoigaku Zasshi. 1985, 39, 214-216.
Spiller HA. Epidemiology of volatile substance abuse (VSA) cases reported to US poison
centers. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2004, 30, 155-165.
Sugie H, Sasaki C, Hashimoto C, Takeshita H, Nagai T, Nakamura S, Furukawa M,
Nishikawa T, Kurihara K. Three cases of sudden death due to butane or propane gas inhalation: analysis of tissues for gas components. Forensic Sci. Int. 2004, 143, 211-214.
Wang F. Assessment of quantum mechanical models based on resolved orbital momentum distributions of n-butane in the outer valence shell, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2003, 107, 10199-10207.